How Fast Charging Technology is Revolutionising EVs
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming the way we drive, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to petrol and diesel cars. However, one of the main concerns for potential EV owners has always been charging time. Unlike refuelling a petrol car, charging an EV traditionally took hours, making long journeys inconvenient. This is where fast charging technology is making a difference.
Fast charging, also known as rapid or ultra-fast charging, has significantly reduced charging times, making EVs more practical for daily use and long-distance travel. As charging technology continues to evolve, it is helping to eliminate range anxiety and encouraging more drivers to switch to electric. In this article, we explore how fast charging works, the benefits it offers, the challenges it faces, and what the future holds for ultra-fast charging technology.
Understanding Fast Charging for EVs
What is Fast Charging?
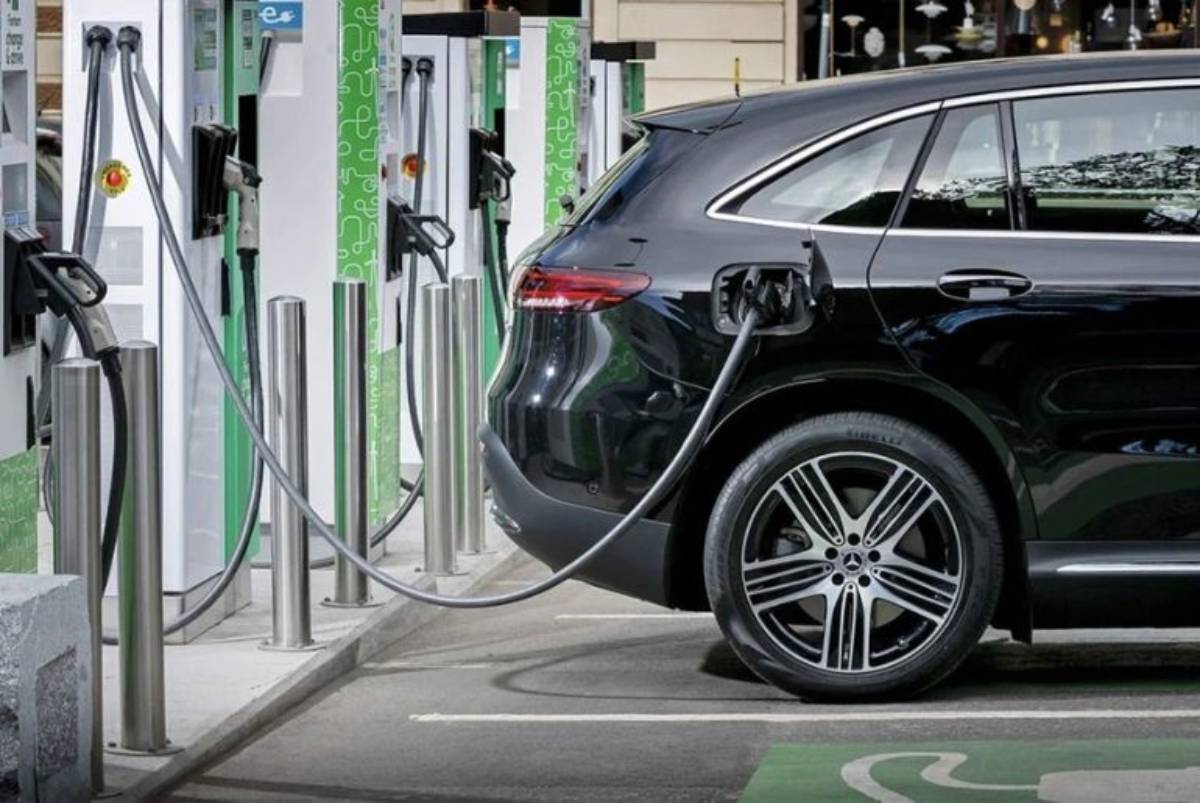
Fast charging refers to the ability to charge an EV battery at a much quicker rate than standard home chargers. While a typical home charger operates at 3-7 kW, fast chargers start at 50 kW and can go up to 350 kW, allowing vehicles to recharge much faster.
How Fast Charging Works
Fast chargers use direct current (DC) rather than alternating current (AC) to charge an EV battery more efficiently. Most home chargers provide AC power, which the car’s onboard converter transforms into DC before storing it in the battery. Fast chargers bypass this process by delivering DC power directly, speeding up the charging process.
The charging speed depends on various factors, including the charger’s power output, the vehicle’s battery capacity, and the car’s ability to accept higher charging rates. Not all EVs can handle ultra-fast charging, so it is important to check a car’s specifications before using these chargers.
The Benefits of Fast Charging
Reduced Charging Time
One of the biggest advantages of fast charging is the reduction in charging time. With traditional home chargers, an EV may take several hours to fully charge. Fast chargers, on the other hand, can provide a significant charge in a matter of minutes.
- 50 kW chargers – Charge a typical EV to 80% in about 45-60 minutes.
- 150 kW chargers – Can provide the same charge in 20-30 minutes.
- 350 kW chargers – Can charge an EV to 80% in as little as 10-15 minutes, depending on battery compatibility.
Convenience for Long-Distance Travel
For many drivers, long trips with an EV have traditionally been a challenge due to long charging times. Fast charging stations located along motorways and key routes make it easier to travel long distances without extended stops. This makes EVs a more viable option for road trips and business travel.
Encouraging EV Adoption
One of the biggest barriers to EV adoption has been charging speed. With fast charging technology improving, more drivers are willing to make the switch from petrol or diesel vehicles. The ability to quickly top up the battery increases confidence in EV ownership.

Quick Guide
Fast Charging at a Glance
- What it is: DC charging at 50kW–350kW, delivering quick top-ups in minutes.
- Charging times:
- 50kW = ~45–60 mins to 80%
- 150kW = ~20–30 mins
- 350kW = ~10–15 mins
- Ideal for: Motorway journeys, road trips, and drivers who need a quick boost.
- Bonus: Growing infrastructure means less range anxiety and more freedom to drive electric.
Pro Tip
Plan your long journeys with fast-charging stops in mind—apps like Zap-Map or A Better Routeplanner can help you map out efficient routes with minimal downtime. And always check your EV’s max charging capacity—350kW stations are only useful if your car can handle it.
Important
Not all EVs can take advantage of ultra-fast charging. Check your vehicle’s peak charging rate before plugging in—using a 350kW charger on a 100kW-capable EV won’t speed things up, but you’ll still pay premium rates.
Challenges of Fast Charging
Battery Degradation
While fast charging is convenient, frequent use of rapid chargers can contribute to battery degradation over time. High charging speeds generate more heat, which can put stress on battery cells. To mitigate this, manufacturers are developing advanced battery cooling systems and improved battery chemistry to handle higher charging speeds more efficiently.
Infrastructure Development
Although fast-charging networks are expanding, they are not yet as widespread as traditional fuel stations. The cost of installing and maintaining high-powered charging stations is significant, and in some areas, access to fast chargers remains limited.
Electricity Demand and Grid Impact
Fast charging requires a large amount of electricity, which can put pressure on the power grid, especially if multiple vehicles charge simultaneously at high speeds. To manage this, energy providers are exploring solutions such as smart charging systems, battery storage, and the use of renewable energy sources.
Future of Ultra-Fast Charging
Advancements in Charging Technology
The future of EV charging looks promising, with new technologies emerging to further reduce charging times. Solid-state batteries, which have a higher energy density and faster charging capabilities than current lithium-ion batteries, could revolutionise EV charging. Additionally, researchers are working on ultra-fast charging solutions that could bring charging times down to just a few minutes, similar to refuelling a petrol car.
Wireless and Automated Charging
Wireless charging is another exciting development in the EV industry. Instead of plugging into a charger, vehicles could charge wirelessly through induction pads embedded in roads or parking spaces. Automated charging solutions, such as robotic arms that connect to EVs without human intervention, are also being explored to improve convenience.
Integration with Renewable Energy
As the world shifts towards renewable energy, integrating solar and wind power with EV charging infrastructure will play a key role in making fast charging more sustainable. Some charging stations are already incorporating solar panels and battery storage to reduce reliance on the grid and lower the environmental impact of EV charging.
Choosing the Right Fast Charging Option
Public Charging Networks
Several companies operate fast charging networks, offering convenient access to rapid charging stations across the country. Some of the leading providers include:
- Tesla Supercharger Network – Exclusive to Tesla vehicles, offering high-speed charging at dedicated locations.
- IONITY – A European fast-charging network providing ultra-fast charging at 350 kW.
- BP Pulse – One of the largest public EV charging networks in the UK.
- Gridserve Electric Highway – Offering rapid charging at motorway service stations.
Fast Charging at Home
While home chargers typically operate at lower speeds, some high-powered home charging solutions are becoming available. For example, 22 kW chargers can provide faster charging times, but they require a three-phase power supply, which is not standard in most homes. Future developments may bring even faster home charging options.
Top 5 FAQs
1. How fast is fast charging compared to standard home charging?
Standard home charging (7kW) can take 8–12 hours. Fast charging (150kW or more) can get you to 80% in as little as 15–30 minutes—ideal for long trips.
2. Will using fast chargers damage my battery?
Occasional use is fine, but frequent fast charging can increase battery wear over time. Many EVs manage heat to reduce impact, and future battery tech is improving durability.
3. Can I install a fast charger at home?
Most homes are limited to 7kW–22kW depending on your electrical supply. 22kW requires a three-phase system, which isn’t standard in UK homes. Ultra-fast home charging isn’t widely available yet.
4. Are fast-charging stations available across the UK?
Yes, networks like BP Pulse, Gridserve, and IONITY are expanding across motorways and major routes. Coverage is growing rapidly, especially in urban areas.
5. What’s the future of EV charging technology?
Expect shorter charging times, wireless charging options, automated plug-in systems, and integration with renewable energy sources. Solid-state batteries will make charging even faster and safer.

Conclusion
Fast charging technology is playing a crucial role in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. By significantly reducing charging times, it is making EVs more practical and convenient for daily use and long-distance travel. Although challenges such as battery degradation and infrastructure limitations exist, advancements in battery technology and charging solutions continue to improve the efficiency and accessibility of fast charging.
As technology evolves, we can expect even faster and more convenient charging options, further cementing EVs as the future of transportation. Whether you’re already an EV owner or considering making the switch, understanding the benefits and limitations of fast charging can help you make the most of your electric vehicle experience.
What are your thoughts on fast-charging technology? Share your experiences and opinions in the comments below!