The Ultimate Guide to Charging Your Electric Car
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, understanding how to charge them is essential for new and prospective EV owners. Unlike traditional petrol or diesel cars, EVs rely on electricity to operate, which means having access to reliable charging solutions is crucial.
Whether you’re wondering how to charge an electric car, the different types of charging stations available, or the best home EV chargers, this guide will cover everything you need to know. We’ll break down the various charging options, explain costs and charging times, and help you choose the best setup for your needs.
Understanding EV Charging: The Basics

Before diving into specific charging solutions, it’s important to understand how EV charging works.
How Does EV Charging Work?
Charging an electric car is similar to charging a mobile phone – you plug it into a power source, and electricity replenishes the battery. However, EVs use different levels of charging, which affect how quickly the battery fills up. The efficiency of charging also depends on factors such as battery size, temperature, and charging technology.
Types of EV Chargers
EV chargers are generally classified into three levels:
- Level 1 Charging (Slow Charging)
- Uses a standard household socket (230V in the UK).
- Provides around 2-3 kW of power, adding 4-5 miles of range per hour.
- Best for overnight charging but not ideal for daily use if you drive long distances.
- Often used as an emergency backup when no dedicated charger is available.
- Level 2 Charging (Fast Charging)
- Requires a dedicated home charger or public charging station.
- Offers 7-22 kW of power, providing 25-75 miles of range per hour.
- The best option for home charging, with installation costs involved.
- Compatible with most EV models and widely available at public charging stations.
- DC Fast Charging (Rapid Charging)
- Found at motorway service stations and public charging hubs.
- Delivers 50-350 kW of power, charging an EV to 80% in 30-60 minutes.
- Ideal for long-distance travel but can be more expensive.
- Uses direct current (DC), which bypasses the car’s onboard charger for faster power delivery.
Home EV Charging: The Best Option for Convenience
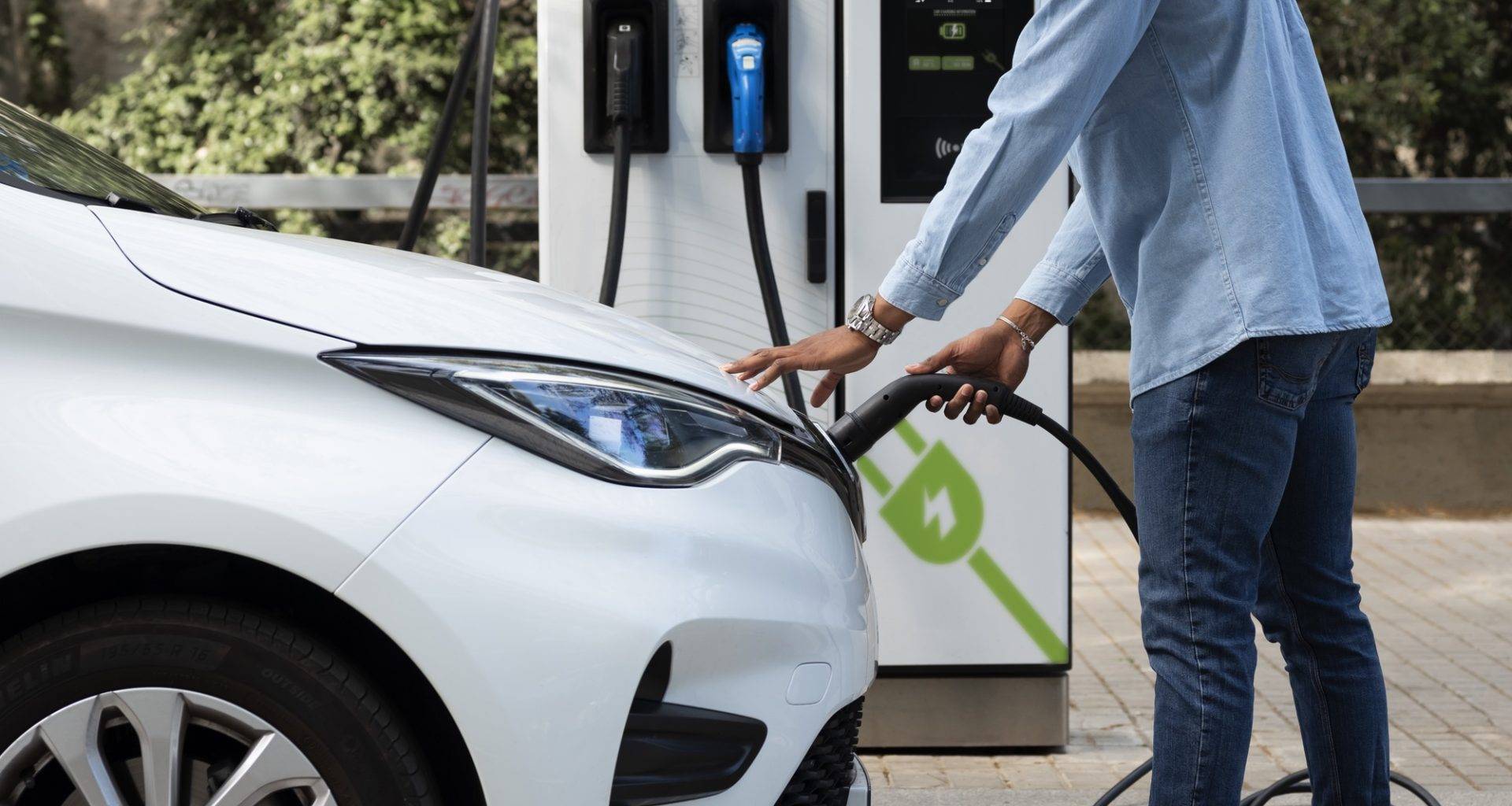

Benefits of Charging at Home
Charging your EV at home is the most convenient and cost-effective option. Here’s why:
- Lower Cost: Charging at home is cheaper than using public chargers, especially with off-peak electricity tariffs.
- Convenience: Plug-in overnight and wake up to a fully charged car without having to visit a public station.
- Safety: Home charging setups are designed to be safe and reliable, reducing the risk of charging-related issues.
- Increased Battery Life: Consistent home charging at moderate speeds helps maintain battery health over time.
Best Home EV Chargers
If you’re considering installing a home charger, here are some of the best home EV chargers available:
- Ohme Home Pro – Smart charging with tariff integration.
- Wallbox Pulsar Plus – Compact design with app control.
- Zappi – Solar-compatible for eco-friendly charging.
- Tesla Wall Connector – Best for Tesla owners.
- Hypervolt Home 2.0 – Stylish and user-friendly.
- Rolec WallPod – Affordable and reliable for basic home charging needs.
Home Charger Installation & Costs
- A standard 7kW home charger costs between £500-£1,000, including installation.
- Some energy providers offer incentives or discounts for charger installations.
- Grants like the EV Chargepoint Grant can reduce costs for certain homeowners.
- Installation should be done by a certified electrician to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Public EV Charging: What You Need to Know
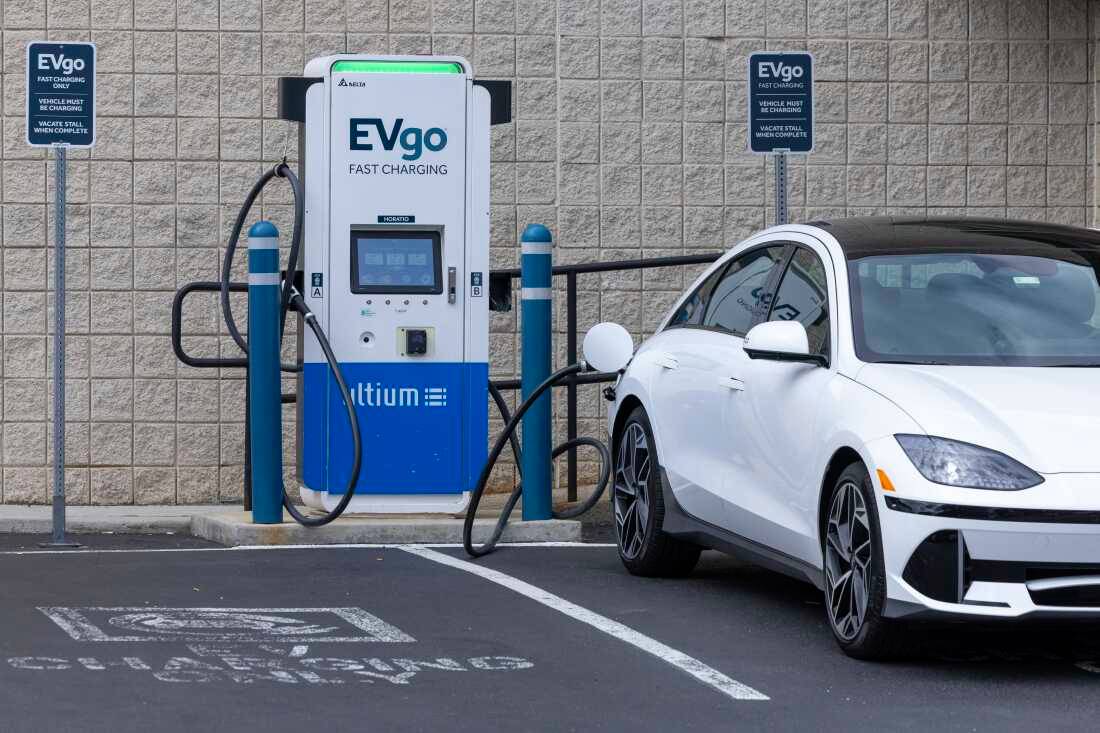

Where Can You Find Public Chargers?
Public charging stations are available in:
- Motorway service stations
- Supermarkets and shopping centres
- Workplace car parks
- On-street locations
- Hotels and leisure facilities
Apps like Zap-Map, PlugShare, and Google Maps help locate charging stations. Many charging networks also offer their own apps for real-time availability updates and payment options.
Cost of Public Charging
- Slow/Fast Charging. Typically 20p-40p per kWh.
- Rapid Charging. Costs range from 50p-80p per kWh.
- Some locations offer free charging, such as supermarkets and workplaces.
- Subscription-based networks may offer reduced rates for frequent users.
- Some ultra-fast charging stations can be significantly more expensive due to their high-speed capability.
How to Use a Public Charger
- Locate a charger using an app.
- Check the connector type and ensure compatibility with your EV.
- Plug in your car and authenticate payment (contactless, app, or RFID card).
- Monitor charging via the app or station display.
- Unplug and continue your journey once charged.
- Be mindful of parking restrictions and overstay fees at high-demand stations.
Charging Speeds and Range Considerations
How Long Does It Take to Charge an EV?
- Home Charging (7kW): 6-8 hours for a full charge.
- Rapid Charging (50kW): 30-60 minutes for 80% charge.
- Ultra-Rapid Charging (150kW+): 10-30 minutes for 80% charge.
Charging time depends on your EV’s battery size, onboard charging capability and the power output of the charger.
Factors Affecting Charging Speed
- Battery size: Larger batteries take longer to charge but offer greater range.
- Charging capacity: Some EVs can’t accept high-speed charging despite using a rapid charger.
- Weather conditions: Cold temperatures can slow down charging efficiency, especially for lithium-ion batteries.
- State of charge: Charging slows down after reaching 80% to protect battery health and longevity.
- Cable type and power source: Some charging cables and stations may have limitations that affect charging speed.
Tips for Efficient EV Charging
- Charge overnight to take advantage of lower electricity rates.
- Pre-condition your battery in cold weather to improve charging efficiency.
- Use a smart charger to schedule charging during off-peak hours for better savings.
- Monitor battery health by avoiding frequent 100% charges, which can degrade battery life.
- Plan long trips in advance using charging station apps to avoid range anxiety.
- Invest in a solar-compatible charger if you have solar panels, allowing for sustainable energy use.
- Carry an emergency charging cable for situations where only a standard socket is available.
Conclusion
Charging an electric car is easier than many think, especially with the right setup at home and access to public chargers when needed. Understanding the different types of chargers, costs, and best practices will help you maximise efficiency and savings.
If you’re considering installing a home EV charger, research the available models and check for grants to reduce costs. For long trips, plan your charging stops to ensure a smooth journey.
Have questions about EV charging? Share your thoughts in the comments!